On-Page SEO 2023: The Beginner’s Guide for WordPress
Table of Contents
Introduction
To ensure that your site is correctly indexed by search engines, it is important to take into account certain elements on your pages. This article about “On-page SEO” is the second in a series of articles on the natural search engine optimisation of a site. In the first one we discussed the indexing methodology of bots. In this one, we will enumerate elements to be optimised on the page in order to maximise your chances to appear in the search engine.
The following are the most important elements to take into account so that your pages are indexed (there are more, but with those listed below you already cover the essentials):
- The title tag
- The “Meta description” tag
-
The
tags The canonical tag URL structure The robots.txt file Structured data Linking in your content The images The User experience
To make the implementation examples in this article concrete, we will use a site built with WordPress. For the simple reason that this blog is built from this CMS. Nevertheless, I make sure that anyone (without or with a WordPress site) will be able to follow along throughout the article.
What is a tag?
Throughout this article we will often use the term “tag”. To simplify things for the moment, remember that it is a field/element that is located in the code of the page. This field is used to describe the content of the page for search engine bots. It is from the information contained in these fields that search engines will make the decision to display your page in relation to a user’s request.
In the context of a site built from WordPress, there are extensions like Yoast that allow you to get these tags implemented without having to manipulate the code. I show you the trick with this plugin for each of the elements.
When building a site, these tags are implemented in the code (HTML). To be able to implement the different tags, in the context of a WordPress site I use an extension called Yoast. The goal is to build my site and implement everything I want without having to touch the code.
1. On-page Optimisation: The title tags
Theory Explanation

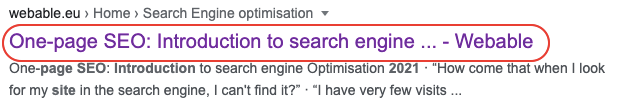
| Recap for the title tags | |
|---|---|
| Length | Between 50 and 60 characters long. When the title is too long, the last part of the text will be cut. |
| The brand name | If the brand name is not the most important keyword of the page, you can put it at the end of the title tag |
| Unique title tag | Have one unique title per page (avoid multiple pages with the same title). Try to include the important keywords in this tag. |
| User oriented | Concretely describe the page’s content using most important keywords. |
Case study of a WordPress site
When you have a WordPress site, you can easily implement title tags thanks to Yoast extension. Once you have activated this extension, you can start filling in the field at the bottom of the image. Then in the “preview as” part of the visualization, you are able to see directly the rendering.
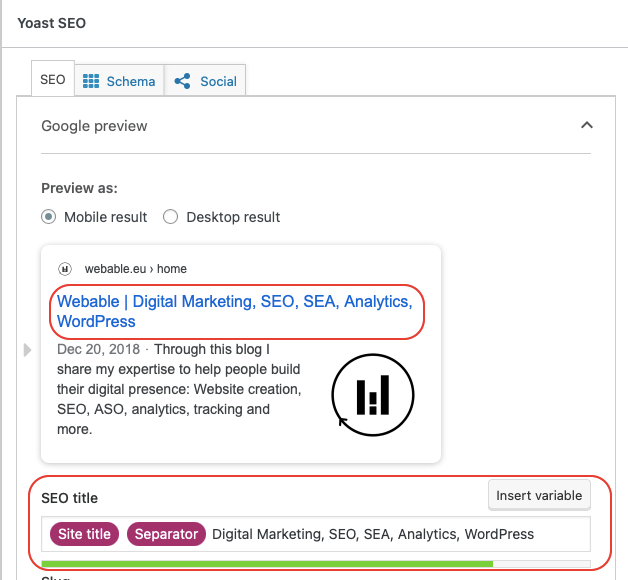
The interesting thing about Yoast is that you can use variables that will fill this field automatically. In theory, you can fully automate the filling of this field. Personally I partially automate to have a level of customization for each article and page.
2. On-page optimisation: The meta description
Theory Explanation
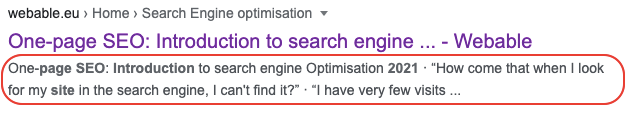
A meta description is a tag that is invisible to the user and that allows crawlers (bots as discussed in the first article) to understand the content of a page. The content of this tag is displayed in the search engine in what is called a “snippet”. In fact, it is usually a contextualization of the title tag (a more in-depth explanation).
| Recap for the Meta Description | |
|---|---|
| Length | Length between 135-160 characters, if the text is too long it will be cut off. Which means that only part of your text will be shown. |
| Unique meta description | Add a custom meta description which is unique from any of your pages. In addition it is recommended to include the most important keywords. You can even reuse some title tag keywords. |
| User oriented | Provide a clear summary of what can be found on the page. |
Case study of a WordPress site
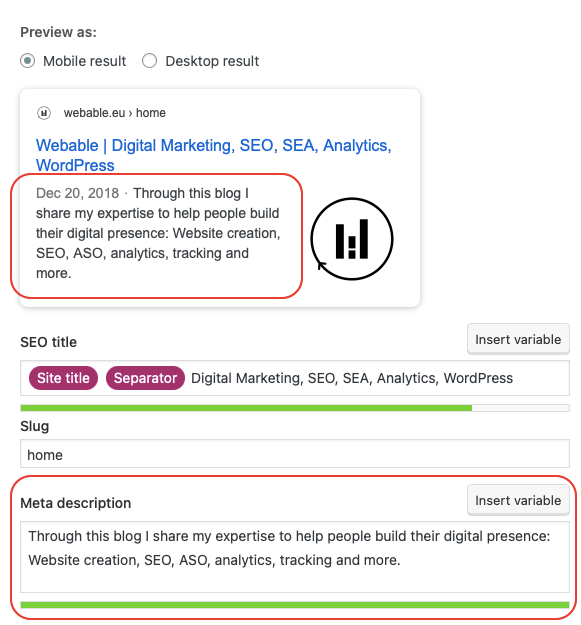
As in the case of the title tag, with Yoast you have for each page or post of your WordPress a field that you can fill without having to touch the code (the extension will take care of it). In addition, just below the field to complete, you have a bar that changes color depending on the number of characters you have. This bar has a green color when you have reached the optimal level, orange when it is slightly below or above, and red when you have overfilled. It is important to note that the text will be cut off if your meta description is too long (it will still be read by the bots).
3. On-page Optimisation : < hn >tags
Theory Explanation
In the indexing of a page, the titles are important. At the hierarchical level, you have the main title and then, the h1,…,h6. These titles allow you to structure your page and for search engines to understand the importance of each title. What is important to remember for this part is that you must structure your text by naming the titles correctly to allow the bots that browse your site to understand faster the structure of your page.
Case study of a WordPress site
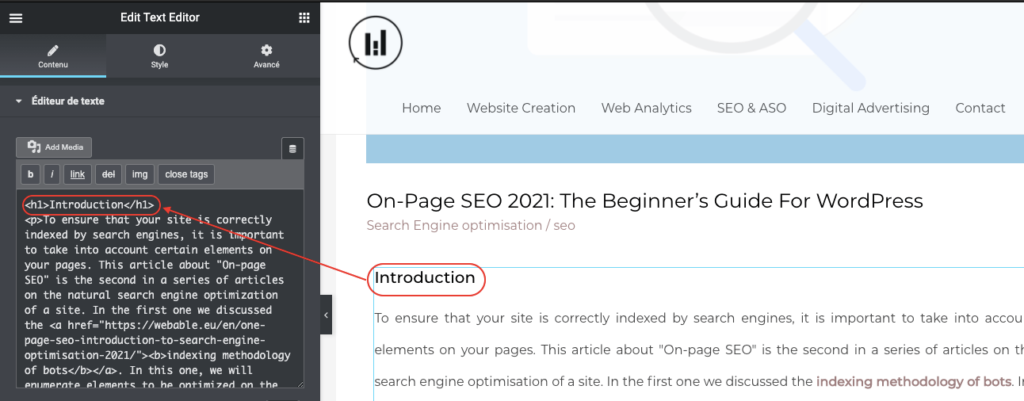
On this blog, I use the extension Elementor for the layout. Even if there are several extensions for the layout, this one is quite handy for all the elements I want to put on the site. As you can see on the picture when I write the text for example “introduction” (in the central part) and I choose to give it the “h2” tag in the text, the Elementor extension translates it directly into the HTML version in the left part. This allows me to have all the title tags without having to touch the code.
4. On-page optimisation: The canonical URL
Theory Explanation
Sometimes a site has the same content in two different segments. This happens for example on sites that cover news. Let’s imagine a site that writes about a cycling race and in the final sprint the favorite falls and gets seriously injured. As a result, the same article can be found not only in the “breaking news” segment, but also in the “sports” segment of the site.
Even if those two articles have two different urls, for Google’s bots it is the same content, with no defined priority. This means that the traffic will be split/diluted between the two pages whereas this is not necessarily what we want. On the article that is in the “sport” segment for example, we will put an element that indicates that it is the main page for this content. Thus the bots will reference this page in priority.
For an eCommerce site, you may need a canonical URL when you have a variation of the same product (different sizes, different colors). In this case, you need to indicate which color should be indexed first.
Case study of a WordPress site
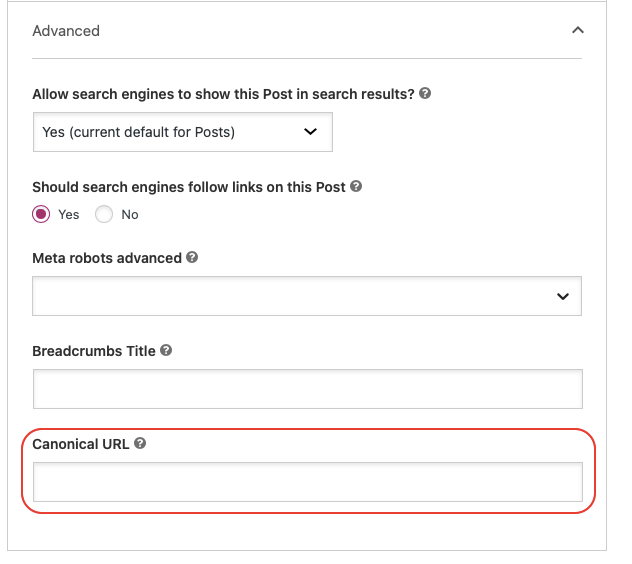
If you have several pages on your site that have the same content, thanks to the Yoast extension you can specify which page you consider as main. In the “advanced” tab of Yoast (on each page or post), you have a field you use to specify the canonical url (as shown in the image below). Then the extension will take care of implementing the tag in the code.
5. On-page Optimisation: URL Structure
Theory Explanation
There some elements to take into account when building an URL:
Understandable for the user: first of all, they must be simple for the user’s understanding.They should contain keywords related to the content of the page and avoid pronouns.
Punctuation: it is recommended to use punctuation via hyphens (-) and underscores (_) in Urls.
Parameters: it is not recommended from a SEO perspective to have urls that contain a lot of parameters as this can hinder the exploration of your website. The reason is that it contributes to the creation of a high number of Urls that link to the same or similar content on your site. In the long run, this can result in the deterioration of the indexing of your site’s content.
Url structure: to solve problems that may be related to dynamic urls it is recommended to use canonical urls.
Case study of a wordpress site
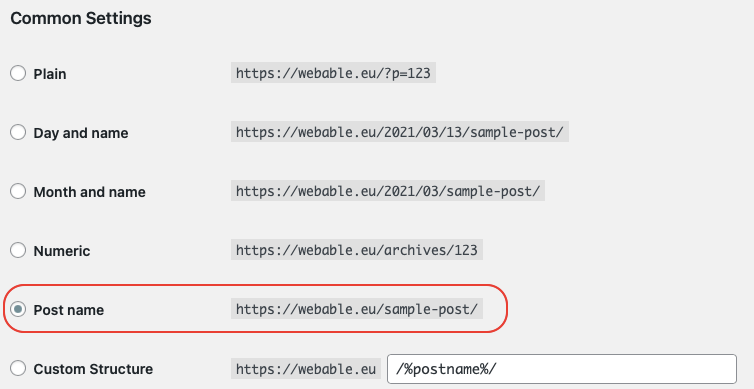
By default, WordPress doesn’t have an SEO-friendly URL structure. By default, you will have the “Plain” so each article will have a reference number, which does not help for the understanding of the content (for users or bots).
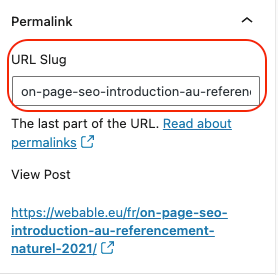
Tip: Personally, to be able to include keywords, which come from the title of the page, for example, I use the option “post name” as shown in the image below which you can set up in the settings > permalinks. Then, if it is necessary to make other customizations of the URL I do it at the level of the “slug” of the page (as on the image below).
6. On-site Optimisation: Robots.txt
To block problematic urls and pages that should not be indexed, the Robots.txt file can be used. It will allow us to block urls that the user does not need to see (such as urls that give access to the site management or archives).
In the case of WordPress sites, you can also indicate the pages you don’t want to index with the Yoast extension.
7. On-page Optimisation: Structured data
Theory Explanation
Structured data allows Google to display in search results additional information about your site’s pages. This can be used to improve the user experience through the arrangement of your site information.
To be able to test structured data for the Google search engine, there is a free tool: Rich Results Test. You can test your structured data with Googlebot for mobile devices (smartphone) and pc (desktop).
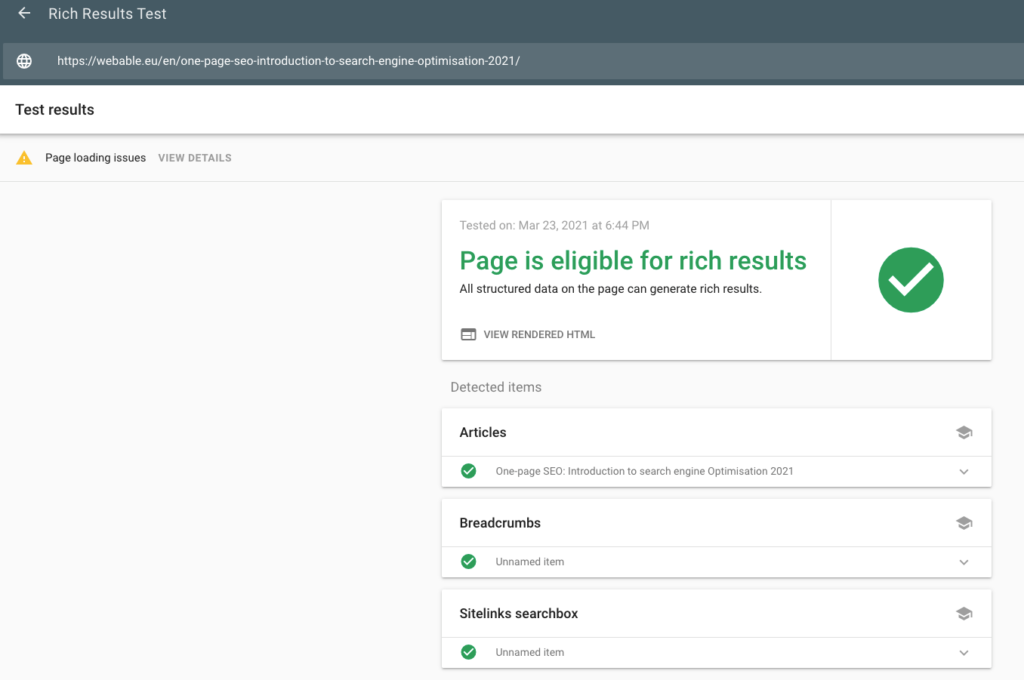
Case study of a WordPress site
In the case of a WordPress site, I also use Yoast to give more context about my content. There is a part that can be defined on each page/post and it’s in the “Schema” part for example for the structured data of the “About us” or “Contact” pages.
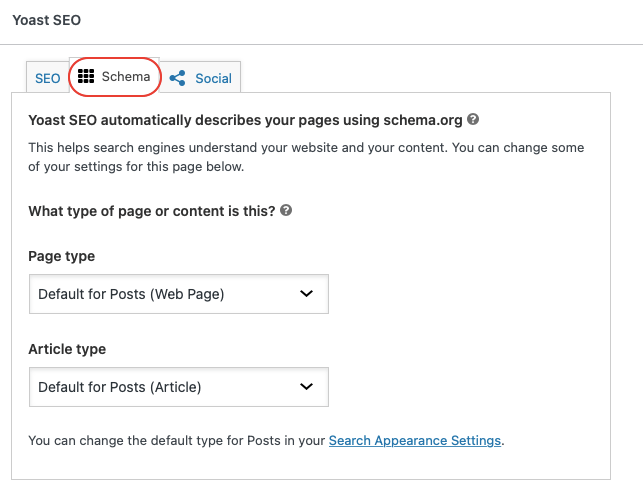
There is another section that can be configured in the Yoast extension settings. In this part, you just have to remember that structured data gives additional context to your page and it can improve your SEO or the way your pages are displayed in the search engine.
8. On-page Optimisation: Link-Building
When you write your content, try to create links between different pages or articles. The reason is that Google bots use these links to discover other content. These links can come from your site or from another site. For example, for this blog, I try to put at least three links per article.
In addition to being convenient for the bots, this allows your users to discover other content on your site and therefore increases the time spent on the site. Since Google tries to suggest interesting articles/sites, the fact that visitors stay long is an indicator of your content quality. Therefore, it can positively influence the SEO of your site.
9. On-page Optimisation: The images
Theory Explanation
Images are indexed by search engines and can represent additional traffic. Even if bots are becoming more and more efficient to understand the content of an image, for the ranking of an image it is recommended to use the “alt text” tag.
Case study of a WordPress site
In the case of a WordPress site, this field exists as soon as you add an image. In my case, as soon as I upload an image I put a description using keywords of the article.
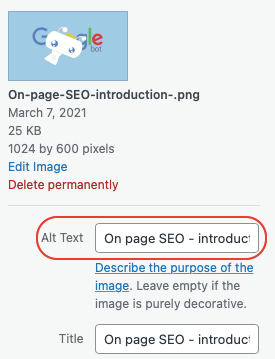
10. Optimisation sur la page : L’expérience de l’utilisateur
Theory Explanation
The user experience on a page can be defined in several ways. Nevertheless, to be able to put a theoretical framework to the subject, we will start from the Google definition. In order to measure the user experience, Google focuses on 5 main elements: Core Web Vitals, Mobile-friendliness, Safe-browsing, secured website, and no intrusive interstitials.
| Page Experience Signals | |
|---|---|
| Core Web Vitals | The page provides a good user experience, focusing on the aspects of loading, interactivity, and visual stability: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. To provide a good user experience, sites should strive to have LCP occur within the first 2.5 seconds of the page starting to load. First Input Delay (FID) : Measures interactivity. To provide a good user experience, sites should strive to have an FID of less than 100 milliseconds. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. To provide a good user experience, sites should strive to have a CLS score of less than 0.1. |
| Mobile-friendly | The page is mobile-friendly. Check if your page is mobile-friendly with the Mobile-Friendly Test. |
| Safe-browsing | The page doesn't contain malicious (for example, malware) or deceptive (for example, social engineering) content. Check to see if your site has any safe-browsing issues with the Security Issues report. |
| HTTPS | The page is served over HTTPS. Check if your site's connection is secure. If the page isn't served over HTTPS, learn how to secure your site with HTTPS. |
| No intrusive interstitials | The content on the page is easily accessible to the user. Learn how interstitials can make content less accessible. |
| Source: Google Search Central | |
Case Study of a WordPress Website
Core Web Vitals
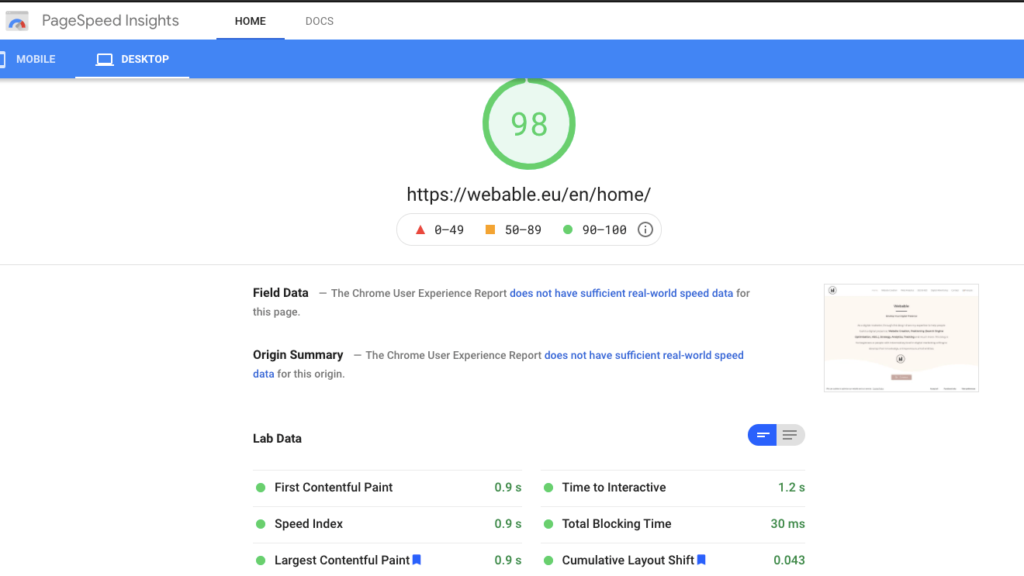
One of the tools that allow you to see the Core Web Vitals of your site is the Google PageSpeed Insight tool. You can measure the three metrics with the LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) to measure the loading time of a page, the CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) to measure the visual stability as well as Total Blocking Time which is actually correlated to the FID (First Input Delay). Yet what to do with this information when it is poor. In a previous article, on optimizing a WordPress site based on PageSpeed Insights, I went through the extensions that allow you to improve these three elements to some extent.
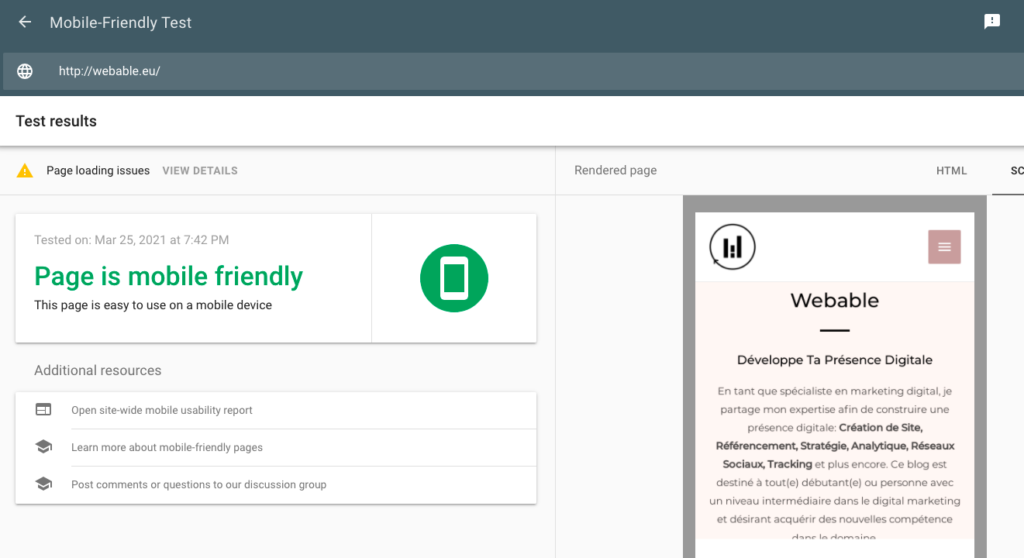
Mobile-Friendly
In WordPress, it has become a standard that themes are adapted to mobile devices. However, you can always check the documentation of the site to make sure this is the case. If you are not sure, as mentioned in the theoretical part of the table, you can always do the test with the Google tool.
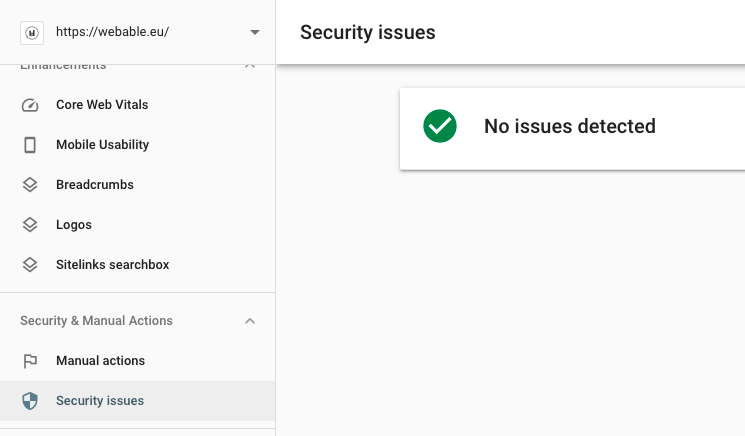
Secure browsing
To check if your browsing is secure, you can use the free Google Search Console tool: Security & Manual Actions > Security Issues.
HTTPS
To have a secured version of your site, symbolized by the small padlock next to the URL, you must have a SSL certificate. This certificate must be activated by the web host of your site. Then to direct your site from the http version to https, in WordPress you can implement a redirection manually on the server, or via the use of an extension. If you are not comfortable with messing around on your server via FileZilla, I recommend using the extension in this case. But, before activating the extension make sure that the SSL certificate is enabled from your host’s interface.
In summary, from a Google point of view, to improve the user experience on a page, it is necessary to take into account the core web signals, the ergonomics of the page on mobiles, avoid phishing systems to ensure a secure browsing. Finally, it is important to have an SSL certificate to keep user data secure, especially on e-commerce sites.
Personally, in addition to the elements mentioned above, I pay attention to the typography and spacing of my texts and images. This makes the articles easier to read.
It is more difficult to measure this aspect of the user experience, but after changing the spacing of my texts (and without publishing any new articles), I looked at whether the average time spent on an article had increased. I had assumed that if the text is unreadable, people won’t necessarily want to finish the text, especially on small formats like mobile.
Conclusion
In order to understand the content, search engine bots read some fields/tags in the code of a page. To help you, I have listed important elements to take into account.
| Item | Priority |
|---|---|
| Title Tag | High |
| Meta Description | High |
| Headers Tags | Medium |
| Canonicals URLs | High |
| Page URL | Medium |
| Robots.txt | High |
| Structured Data | Medium |
| Link-Building | High |
| Images | Medium |






